Hearing Rights for All: Auracast's Promise of an Inclusive Tomorrow!
[TAIWAN, 03rd Jun. 2025]
As someone with elderly family members grappling with hearing loss, the introduction of Auracast technology, as detailed in this report, sparks a profound sense of anticipation. It's not just about clearer audio; it's about fundamentally transforming accessibility and, crucially, diminishing the persistent stigma often associated with hearing aids and assistive listening devices. The "Auracast" report by RNID (Royal National Institute for Deaf People) paints a compelling picture of how this new Bluetooth LE Audio standard can usher in a more inclusive world. For families like mine, witnessing the daily challenges and occasional social isolation faced by loved ones due to hearing difficulties, the promise of Auracast to provide seamless, high-quality audio in various settings is incredibly exciting. Beyond the technical advancements, the true revolution lies in its potential to foster greater participation and reduce the feeling of being "othered," making it a deeply personal and hopeful development.
The "Auracast" report, published by RNID, introduces Auracast as a new technology poised to revolutionize audio accessibility, particularly for the over 18 million people in the UK who are deaf, have hearing loss, or tinnitus. The report emphasizes Auracast's potential to create a more inclusive world by transforming access to health, employment, transport, and culture for a wide range of individuals, including those who are blind, partially sighted, or non-native speakers.
Key Aspects of Auracast:
- Problem Addressed: Current assistive listening systems (ALS) face challenges like limited availability and poor maintenance, making it difficult for people with hearing loss to understand speech, especially in noisy environments.
- The Solution: Auracast is an industry-agreed standard based on Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) Audio, enabling high-quality audio to be broadcast to various devices such as hearing aids, earbuds, and smartphones. This technology can be incorporated into both consumer and prescription hearing devices.
- How it Works:
- Transmitters: Auracast transmitters can be personal devices (TVs, phones, tablets, computers) or public systems (lecture halls, gyms, train stations). They send one or more audio streams, along with "advertising information" (metadata like broadcast name and encryption status). For privacy, streams can be encrypted, requiring a password.
- Receivers: Auracast receivers, often earbuds or hearing aids, pick up the digital audio stream and convert it to audio.
- Assistants: An Auracast assistant (e.g., a smartphone app or smartwatch) helps receivers select the correct audio stream, especially when multiple broadcasts are present.
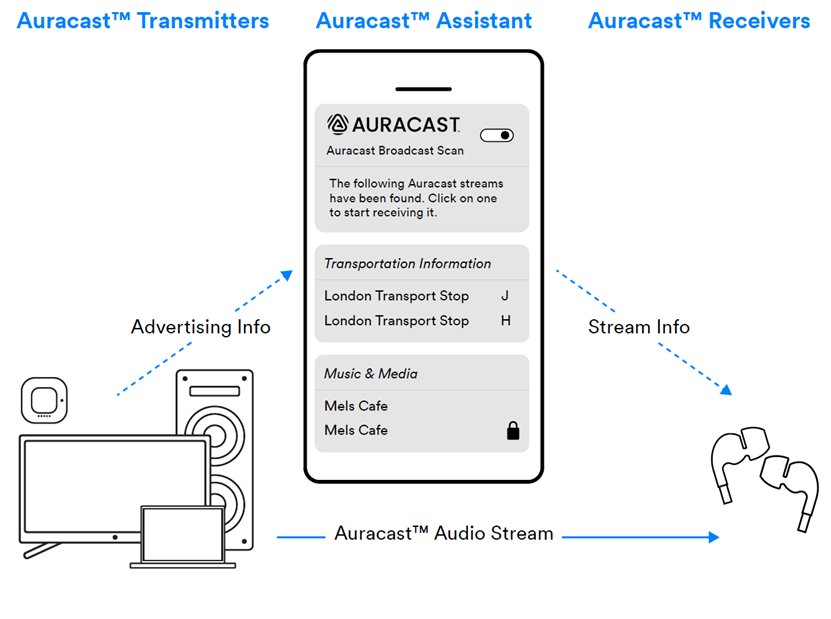
Image source: SIG Tech article “How to Design Auracast™ Earbuds”
- Benefits: Auracast offers wider access to assistive listening, reduces stigma, lowers costs due to a larger user base and smaller hardware, and improves reliability with easier fault detection.
- User Interfaces: The report emphasizes the importance of inclusive design for user interfaces, recommending various stream selection paradigms such as "pick-from-list" (screen-based), "step-through-list" (button-based), NFC, and QR codes, to ensure accessibility for all users, including those without smartphones.
The report provides detailed use cases, such as watching TV with family, tour guides, exercise classes, hybrid meetings, social gatherings, GP consultations, and public transport, to illustrate Auracast's potential and highlight considerations for stakeholders.
Full RNID report: https://rnid.org.uk/2025/02/auracast-a-revolution-in-audio-accessibility/
For more information about our Bluetooth wireless module and other products, please visit our website or contact our sales team. email
Edited by Intl. Commercial Development Manager: Mr. Tim Chien