Bluetooth's Secret Weapon: Channel Sounding vs. AoA/AoD – Which Tech Reigns Supreme in Location Accuracy?
[TAIWAN, 04th Aug. 2025]
Bluetooth Channel Sounding vs. Bluetooth AoA/AoD: Similarities and Differences
Bluetooth Channel Sounding (CS) and Bluetooth Angle of Arrival (AoA) / Angle of Departure (AoD) are both advanced technologies aimed at improving Bluetooth's ranging and positioning accuracy. However, they differ significantly in their underlying principles, applications, and advantages.
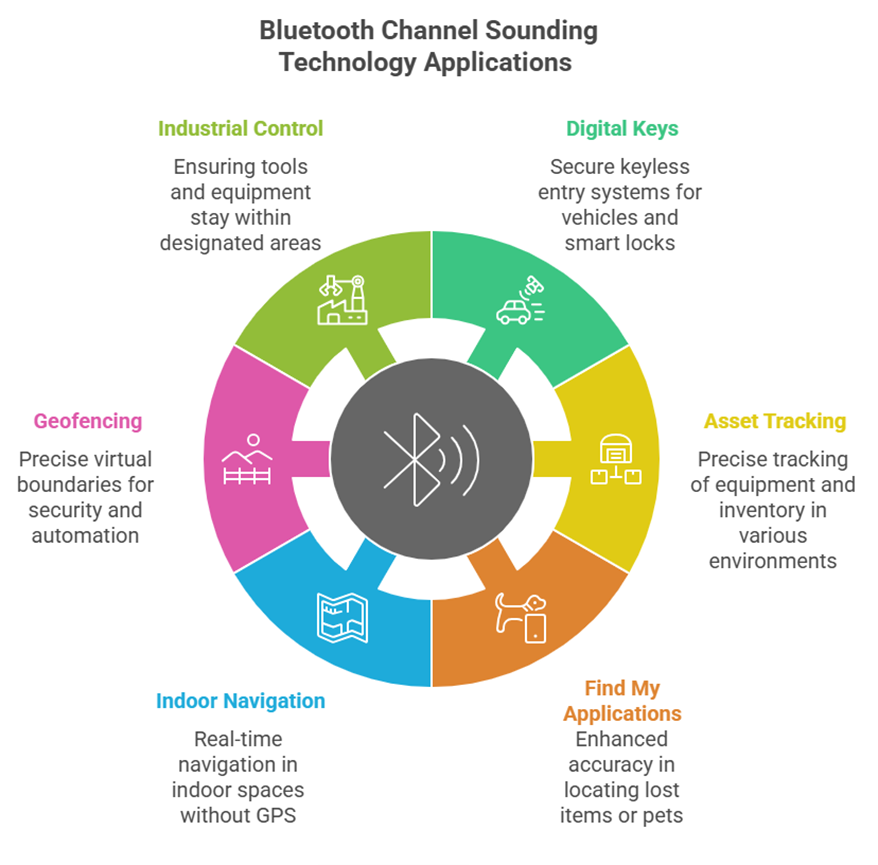
Bluetooth Channel Sounding (CS) Applications
Bluetooth Channel Sounding (CS) is a newer ranging technology that precisely calculates the distance between two Bluetooth devices by measuring phase differences (PBR, Phase-based ranging) and Round-Trip Time (RTT) across multiple radio channels. It aims to provide centimeter-level distance awareness.
Applications:
· Digital Keys and Access Systems: Offers highly secure, keyless entry for vehicles or smart locks, ensuring access only when an authorized device is within a specific, verified range.
· Asset Tracking and Management: Precisely tracks equipment, inventory, or high-value assets in environments like warehouses, factories, or logistics centers, improving efficiency and preventing loss.
· "Find My" Applications: Significantly enhances the accuracy of finding lost items or pets, providing not just proximity but also more precise location information.
· Indoor Navigation and Positioning: Delivers real-time, high-accuracy navigation in indoor environments where GPS signals are unreliable, such as shopping malls, airports, or hospitals.
· Geofencing: Creates more precise virtual boundaries for security management, restricted access, or triggering location-based automated actions.
· Industrial Control and Safety: Ensures tools or equipment remain within designated areas, triggering alerts or even lock-down functions if moved outside.
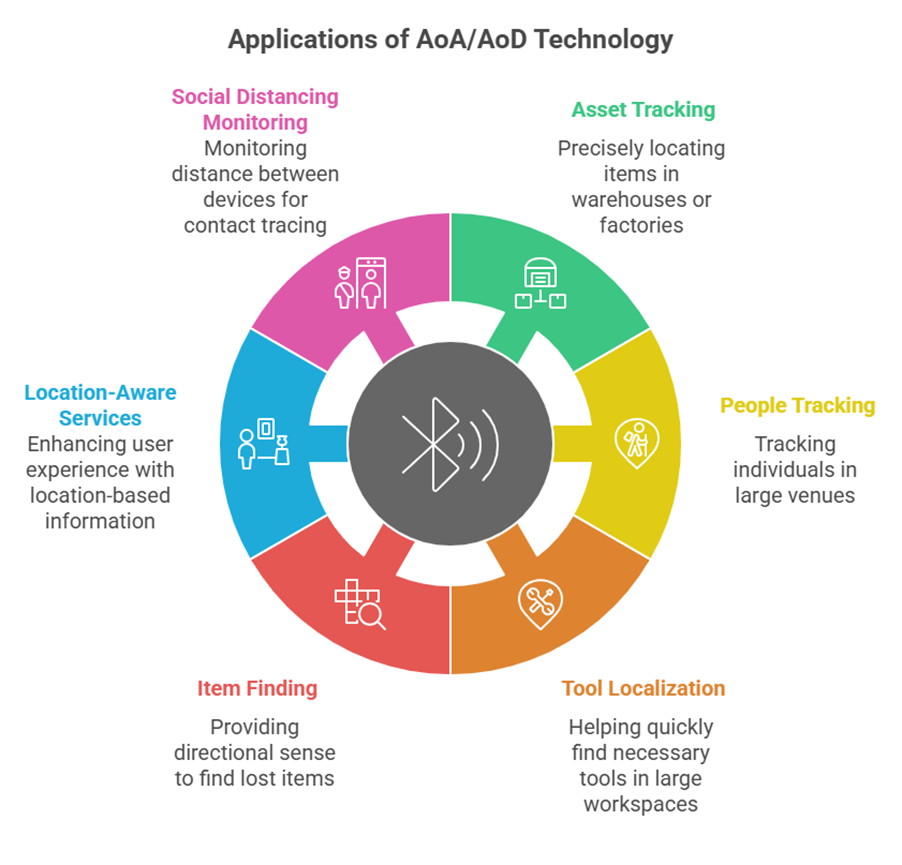
Bluetooth AoA/AoD Applications
Bluetooth Angle of Arrival (AoA) and Angle of Departure (AoD) are direction-finding technologies introduced in the Bluetooth 5.1 standard. They enable positioning by analyzing the angle at which a radio signal arrives or departs.
· AoA (Angle of Arrival): A signal is sent from a single-antenna device and received by a multi-antenna array. The direction of arrival is calculated by measuring the phase differences of the signal across the different antennas.
· AoD (Angle of Departure): A signal is sent from a multi-antenna array, and a single-antenna receiver calculates its own direction relative to the transmitting device by measuring the phase differences of the signals emitted from the different antennas.
Applications:
· Indoor Positioning Systems (IPS) & Real-Time Locating Systems (RTLS):
o Asset Tracking: Precisely locating items in warehouses or factories to improve management efficiency.
o People Tracking: Tracking individuals in large venues like shopping centers or exhibition halls, or providing indoor navigation.
o Tool Localization: Helping quickly find necessary tools in large workspaces.
· Item Finding Applications: Similar to Channel Sounding, but AoA/AoD focuses more on providing "directional sense," such as pointing towards a lost item.
· Location-Aware Services: For example, museum guides where users can point their phone at a specific exhibit to get more information.
· Social Distancing Monitoring: In specific applications, monitoring the distance and direction between devices for purposes like contact tracing.
Similarities
1. Enhanced Positioning Accuracy: Both aim to surpass traditional Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI)-based positioning methods, offering sub-meter or even centimeter-level accuracy.
2. Indoor Positioning Applications: Both are highly suitable for indoor environments where GPS signals are unavailable, addressing the challenges of indoor localization.
3. Asset Tracking and "Find My" Solutions: Both have the potential for applications in tracking physical items or locating lost devices.
4. Increased Security: By providing more precise distance or direction information, both can enhance the security of applications like digital keys and access control.
5. Based on Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE): Both leverage BLE technology, making them power-efficient and suitable for battery-powered IoT devices.
Differences
|
Feature |
Bluetooth Channel Sounding (CS) |
Bluetooth AoA/AoD |
|
Measurement Principle |
Measures signal phase and Round-Trip Time (RTT) to directly calculate the distance between two points. |
Measures the Angle of Arrival (AoA) or Angle of Departure (AoD) to determine the signal's direction, then uses multiple angles for positioning (triangulation). |
|
Hardware Required |
Typically requires more complex radio modules to process multi-channel phase and time measurements. Theoretically single antenna can do ranging, but an optimized antenna setup may still be needed for better accuracy. |
The receiver (AoA) or transmitter (AoD) requires a multi-antenna array to measure phase differences. |
|
Primary Output |
Distance |
Direction |
|
Accuracy |
It can achieve centimeter-level accuracy, often considered the highest ranging accuracy currently available in Bluetooth technology. |
Can achieve sub-meter (sub-foot) accuracy, roughly 10-30 cm, depending on the antenna array configuration and environment. |
|
Security |
Has stronger built-in anti-relay attack capabilities, as it considers the signal's round-trip time. |
Potentially more susceptible to man-in-the-middle attacks, as it primarily relies on signal strength and phase differences to infer distance or direction. |
|
Complexity |
More complex to implement, requiring processing of multi-channel phase and timestamps. |
Hardware (antenna array) and algorithms are relatively complex, leading to higher deployment and maintenance costs. |
|
Application Focus |
More focused on precise distance perception and secure access control scenarios requiring extremely high distance accuracy. |
More focused on precise direction perception, for example, tracking moving objects indoors or providing direction-based navigation. |
|
Standard Introduction |
Bluetooth 6.0 |
Bluetooth 5.1 |
Conclusion
In essence, Bluetooth Channel Sounding excels at providing extremely precise distance measurements and offers security advantages, making it particularly well-suited for applications like digital keys and high-security access control where relay attacks must be prevented. Bluetooth AoA/AoD, on the other hand, focuses on providing accurate direction determination. By using multiple directional inputs, it enables positioning that's widely applied in indoor asset tracking and navigation where knowing "which direction" an object is in is crucial. While both aim to enhance Bluetooth positioning accuracy, their underlying technical principles and the type of information they output differ. This makes each more advantageous in specific application scenarios. When deploying, the choice between them will depend on the specific requirements of the application.
Edited by Intl. Commercial Development Manager: Mr. Tim Chien
📢 Get Ready for Our Latest Episode of BLE Tech Pulse Decoded on Aradtube!
Subscribe to our channel and hit that notification bell so you don't miss our newest video releases.
🔗 YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@Aradconn