Zigbee Communication Protocol: The Lightweight Pioneer of IoT
[TAIWAN, 19th Sep. 2025]
1. Introduction: The Cornerstone of the Internet of Things
In the rapidly evolving world of the Internet of Things (IoT), device connectivity has become the norm. However, when faced with hundreds or thousands of sensors and controllers that require long-term, stable operation and are highly sensitive to power consumption, traditional technologies like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth often fall short.
This is where Zigbee excels. It is a low-power, low-cost, short-range wireless communication protocol based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. Zigbee was specifically designed to fill the gap left by Wi-Fi and Bluetooth in large-scale, low-power wireless sensor networks, making it an ideal choice for smart homes, industrial automation, and more.
2. Core Technical Analysis
i. Physical and MAC Layers
The foundation of the Zigbee protocol is the IEEE 802.15.4 standard, which is specifically designed for Low-Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks (LR-WPAN). Operating primarily in the 2.4 GHz frequency band, Zigbee uses a CSMA/CA (Collision Avoidance) mechanism to ensure reliable communication.
ii. Network Layer: The Robust Mesh Network
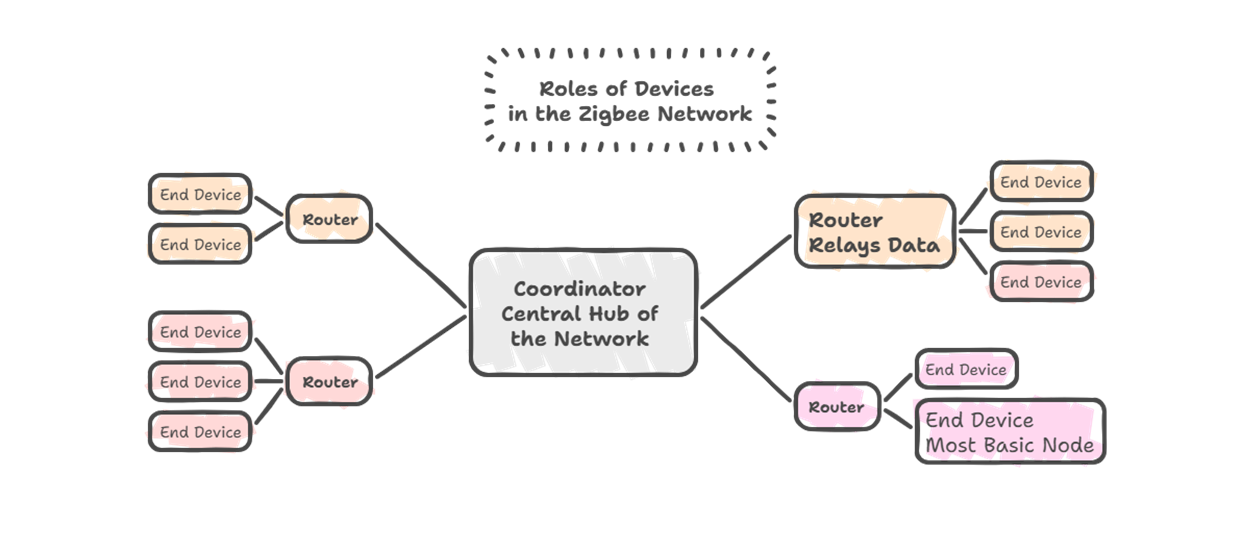
Zigbee's most notable feature is its Mesh Network architecture. This network model allows each device (node) to not only communicate with a coordinator but also act as a repeater, forwarding data to other nodes. This provides two key advantages: extended network range and enhanced network robustness.
In a Zigbee network, devices assume different roles:
· Coordinator: The central hub of the network.
· Router: Relays data and extends the network range.
· End Device: The most basic node, designed for ultra-low power consumption with long sleep periods.
iii. Application Layer and Security
To ensure interoperability between different manufacturers' devices, the Zigbee Alliance created the Zigbee Cluster Library (ZCL). This standardizes common device functions, enabling seamless cross-vendor communication. For security, Zigbee uses the industry-standard AES-128 encryption algorithm to provide robust data protection.
3. In-Depth Analysis of Zigbee vs. BLE Applications
In the IoT landscape, Zigbee and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) are two common low-power protocols. While both can be used for sensors and controllers, their application scenarios and strengths are distinctly different.
|
Feature |
Zigbee |
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) |
|
Network Topology |
Mesh network |
Point-to-point or star network, can also be a mesh network (Bluetooth Mesh) |
|
Primary Use |
Large-scale, highly stable smart home and industrial IoT networks |
Direct communication with smartphones, wearables, and electronic tags |
|
Power Consumption |
Extremely low power, End Devices can deeply sleep for years |
Very low power, suitable for battery-powered devices, but varies with communication frequency |
|
Advantages |
- Robust and self-healing mesh network for high reliability - Scalable to a massive number of devices |
- Direct communication with smartphones, no extra gateway needed - Relatively simple protocol with a lower entry barrier for development |
|
Disadvantages |
- Typically requires a dedicated gateway - More complex protocol stack |
- The early mesh network was less mature - Interoperability between brands can be a challenge, but Matter is improving it |
Application Examples:
· Zigbee is suitable for: A complete smart home system with over 50 sensors, switches, and lights. Its mesh network ensures stable communication for all devices. Even if some devices fail, the network can self-heal, guaranteeing long-term reliability.
· BLE is suitable for: A single smart light bulb controlled individually, or a smart lock that needs to be unlocked via a phone app. In such point-to-point interactions, BLE’s convenience outweighs the need for a Zigbee gateway.
In fact, many smart home products on the market offer both Zigbee and BLE versions, or even support both protocols. simultaneously to meet the needs of different users.
4. Conclusion and Future Outlook
In conclusion, Zigbee has secured an indispensable place in the IoT ecosystem thanks to its unique low-power, mesh networking capabilities. Despite competition from BLE, the two technologies are often complementary rather than competing in many applications.
With the advent of new protocols like Matter, IoT interoperability will reach a new level. Zigbee will continue to play a crucial role as a core technology within the Matter protocol, particularly in the domain of low-power, large-scale networks.
Image and Text Copyright Statement:
All text and image content in this article (including but not limited to headings, body text, analysis, and summaries) are the copyright of Arad Connectivity Co., Ltd. Any form of reproduction, reprinting, modification, or commercial use without written authorization is strictly prohibited.
📢 Get Ready for Our Latest Episode of BLE Tech Pulse Decoded on Aradtube!
We're diving deeper into this fascinating topic! Subscribe to our channel and hit that notification bell so you don't miss our latest video releases.
🔗 YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@Aradconn
Edited by Intl. Commercial Development Manager: Mr. Tim Chien